Our Services - BPPV (benign paroxysmal positional vertigo)
Effective BPPV Treatment
How can our Physiotherapists help?
Our physiotherapists are highly experienced in providing effective and personalized BPPV treatment. Our dedicated team understands the profound impact that Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV) can have on your daily life, from the spinning sensation when moving in and out of bed to persistent unsteadiness during the daytime.
Through our tailored BPPV physio approach, we aim to quickly alleviate your dizziness and vertigo, improving both vestibular function and overall balance. BPPV treatment is typically fast, non-invasive, and highly successful.
Symptoms, Treatments and Approach
What is Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV)?
BPPV is one of the most common vestibular disorders worldwide, characterized by sudden, brief, and intense episodes of vertigo. This dizziness is typically provoked by specific head movements, such as rolling over in bed, lying down, or looking up. Patients often describe a sensation of spinning or sinking.
The Cause of BPPV
BPPV occurs when tiny crystals of calcium carbonate, known as otoconia (or "ear rocks"), become dislodged from their usual location (the utricle) within the inner ear and move into one of the semicircular canals. These dislodged crystals interfere with the normal fluid movement inside the canal, sending confusing signals to the brain and causing the sensation of spinning or vertigo, particularly when the head is moved into certain positions.
Causes and Risk Factors for BPPV
Understanding the cause helps guide the best BPPV treatment plan:
Idiopathic BPPV
The cause is unknown, which accounts for most of the cases
Secondary BPPV
Arises as a consequence of other vestibular-related or conditions such as, head trauma, Meniere’s disease, vestibular neuritis, middle ear infection, etc
Aging
Incidence of BPPV increases with age due to natural degeneration of the inner ear structures, particularly in individuals over 60
Recognizing the Symptoms of BPPV
The symptoms of BPPV are distinct and typically manifest during simple, rapid head and body movements. If you suspect you need BPPV physio, you may experience:
Vertigo or spinning sensation when rolling over in bed, tilting the head back to look up, or bending over.
The spinning sensation usually lasts from a few seconds to about a minute.
Nystagmus (involuntary, rapid eye shaking) during an episode.
Balance difficulties, particularly in visually stimulating or crowded areas.
Occasional nausea and vomiting during severe episodes.
While these episodes can be accompanied by anxiety, it is vital to remember that BPPV is a common, non-threatening condition that can be treated successfully by a vestibular physiotherapist.
How is BPPV Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of BPPV involves a thorough evaluation by our experienced BPPV physio team. The assessment includes:
Medical History Review: Discussing the onset, duration, and triggers of your vertigo.
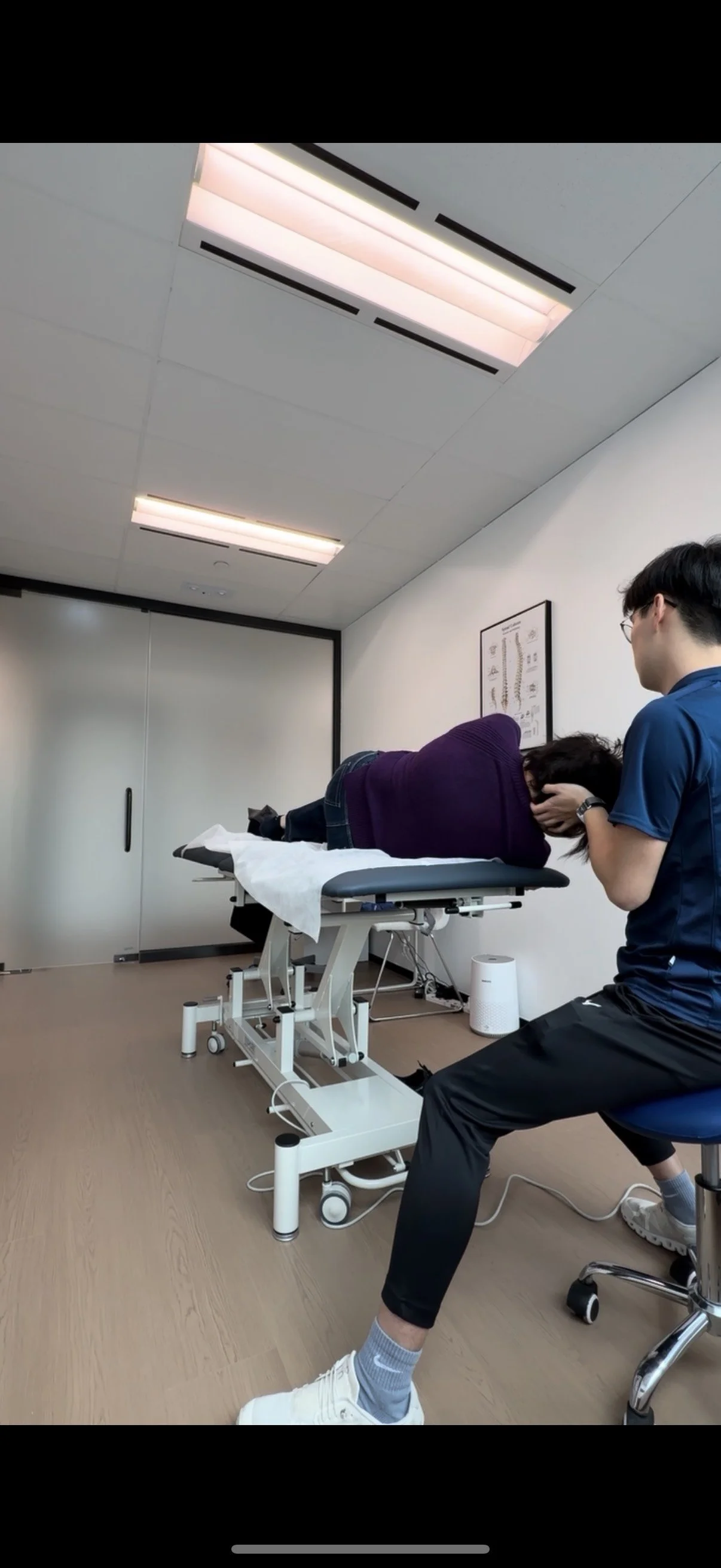
The Dix-Hallpike Test: This specific diagnostic maneuver is performed by the physiotherapist to quickly elicit vertigo symptoms.
Nystagmus Observation: The intensity and direction of the involuntary eye shaking (nystagmus) are carefully observed. This crucial observation confirms the diagnosis and pinpoints exactly which semicircular canal (e.g., posterior, horizontal, or anterior) is affected, guiding the choice of the appropriate BPPV treatment.
BPPV Treatment: The Canalith Repositioning Maneuvers
The definitive BPPV treatment is a series of precise Canalith Repositioning Maneuvers (CRMs). These physical maneuvers are specifically designed to gently steer the dislodged crystals (otoconia) back into their correct location within the inner ear (the utricle), providing rapid relief from dizziness and vertigo.
The Epley Maneuver
The posterior canal is the most commonly affected location in BPPV, making the Epley Maneuver the most common and effective BPPV treatment.
How to Perform (Demonstrated by Your BPPV Physio):
Start Sitting Up: Sit upright on a bed, turning your head 45 degrees toward the affected ear.
Lie Back Quickly: While keeping your head turned, lie back quickly on your back, with your shoulders on the bed and your head reclined over the edge. Hold this position for about 40 seconds until the vertigo subsides.
Turn Your Head: Turn your head by 90 degrees to the opposite side without lifting it off the bed. Hold this position for another 40 seconds.
Roll Over: Roll over onto the same side your head is facing. Hold this position for 40 seconds until the vertigo subsides as well.
Sit Up: If you feel ready, sit back up while keeping your head in the same direction and tilted downwards.